Cloud hosting has become an essential foundation for modern websites and applications.
However, many small business owners and startups still find the concept confusing.
What exactly is cloud hosting? How does it work? And is it the right choice for your needs?
This beginner’s guide breaks down the key aspects of cloud hosting in simple terms.
Whether you’re considering migrating your website to the cloud or launching a new cloud-native application, you’ll learn the pros and cons to evaluate if it’s the best hosting approach for you in 2024 and beyond.
Table of Contents
What is Cloud Hosting?

Cloud hosting refers to deploying and running websites, mobile or web apps, databases, and other services using virtualized, distributed servers offered by cloud providers such as Amazon, Microsoft, and Google.
Instead of owning your own physical VPS or dedicated server, you access shared computing resources managed by the cloud provider.
They take care of maintenance, security, software updates, and load balancing across data centers worldwide.
Your website is hosted “in the cloud”, meaning the global network of data centers owned by the cloud company you choose.
It allows your site to leverage tremendous computing power on demand.
The benefits of cloud hosting include:
- Scalability to handle spikes in traffic
- Redundancy and uptime with automatic failover
- Pay-as-you-go costs rather than fixed server expenses
- Access to enterprise-level infrastructure
- Improved collaboration from anywhere with internet access
With cloud hosting, you essentially rent computing resources like storage, RAM, and CPU power from large data center operators.
It provides tremendous flexibility, allowing you to scale up or down your website hosting as needed.
Rather than purchasing physical servers outright, you pay only for the amount of cloud resources you actually consume.
This “pay-as-you-go” approach avoids upfront capital expenditures and helps optimize costs.
How Does Cloud Web Hosting Work?
Now that you understand what is cloud hosting, let’s see the basics of how it works.
Traditional web hosting relies on a single physical server to host a website. This server is located in a data center and connected to the internet.
All the website’s files, databases, and computing resources are hosted on this one server.
The problem with this shared hosting model is that it has LIMITED scalability.
If your website experiences a spike in traffic, that single server may become overloaded and crash.
Cloud hosting follows a completely different model.
Instead of being hosted on a single server, your website is hosted on a network or “cloud” of servers that are connected together.
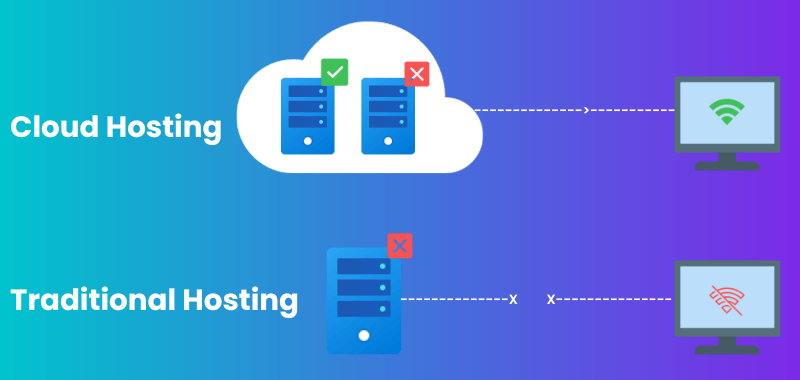
This cloud of servers is maintained by the cloud hosting provider, such as Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud.
They handle provisioning and managing the servers, allowing you to focus on your application and content.
When a visitor wants to access your website, their request is routed to the closest available server in the cloud network. This server will then deliver the hosted files and data for your site.
If one server experiences high demand, the load is automatically distributed across the other servers in the network.
This makes cloud hosting extremely scalable – it can handle any amount of traffic by simply adding more servers to the cloud.
In addition to better scalability, cloud hosting provides built-in redundancy and disaster recovery.
Even if one server fails, the network will automatically reallocate traffic so that the website remains available and online.
Now let’s take a deeper look at the different types and models of cloud hosting available.
Types of Cloud Hosting
There are several ways to categorize the different types of cloud hosting services available today.
We will focus on two common classifications;
- Cloud Deployment Models
- Cloud Service Models
1. Cloud Deployment Models
Deployment models refer to the type of infrastructure, security, and accessibility for a cloud environment.
There are three main Cloud deployment models:
1. Public Cloud
- It is owned and operated by third-party cloud providers
- Services offered over the public internet
- Examples – Amazon Web Service, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud
With public cloud hosting, you utilize servers and infrastructure owned by providers like Amazon or Google.
It is an extremely flexible and cost-efficient option, allowing you to scale seamlessly.
However, there are some security concerns around public cloud hosting since you are essentially renting hardware and resources that are shared with other customers.
2. Private Cloud
Private cloud hosting implies using cloud technology like virtualization to create a computing environment hosted within your own data center.
It offers greater customization control and is best suited for organizations with specific security and compliance needs.
The downside is that private clouds require considerable investment and IT expertise to set up and manage.
Cost savings are also minimal compared to using a public cloud provider.
3. Hybrid Cloud
- Combines both public and private cloud infrastructure
- Allows data portability between the environments
- Example – Storing sensitive data on private servers and non-sensitive data on the public cloud
As the name suggests, hybrid cloud hosting means using a combination of public and private cloud platforms.
This provides even more flexibility and allows you to optimize both cost efficiency and customization.
For instance, you can host your website on Amazon Web Services for scalability but keep customer databases on a private server for added data security.
2. Cloud Service Models
In addition to deployment models, cloud services are also categorized into three types of service models:
1. IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
- Provides basic building blocks for cloud IT like servers, storage, and networking
- Highly flexible and scalable
- Examples – Microsoft Azure, Google Compute Engine, Amazon EC2.
IaaS gives you complete control over the software and applications, while the cloud provider maintains the underlying physical hardware.
It is the closest to managing your own physical server infrastructure – but without having to actually purchase or maintain your own hardware.
2. PaaS (Platform as a Service)
- Provides ready-to-use development environments and tools
- Allows you to focus just on your code and applications
- Examples – AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine, Windows Azure, Heroku
PaaS solutions provide pre-configured platforms and development tools optimized for various coding languages like Java, Python, and .NET.
This saves considerable time compared to setting up the underlying infrastructure from scratch.
The cloud provider handles OS updates, security patches, and resource provisioning, allowing your team to simply deploy applications on top of the platform.
3. SaaS (Software as a Service)
- Provides access to complete end-user applications
- Apps are accessible from any device with an internet connection
- Examples – Google Workspace, Google Sheets, Google Slides, and Google Drive
SaaS products are highly user-friendly, allowing even non-technical users to access full-featured apps through their web browser or mobile app.
Since the software vendor takes care of all hosting, maintenance, and updates, you can use the solutions immediately without any complex configurations.
Monthly or annual subscriptions provide access to the SaaS apps.
Benefits of Cloud Hosting
Now that you understand the different types of cloud hosting, let’s look at some of the key benefits driving its immense popularity:
1. Cost Savings
Cloud hosting completely eliminates the high capital expenditure of purchasing physical servers and data center infrastructure.
Instead, you pay-as-you-go based on actual usage, leading to significant cost savings.
2. Scalability
Provisioning additional cloud hosting resources takes just minutes, allowing you to easily scale up or down based on dynamic demands. This scalability also handles traffic spikes during peak seasons.
3. Reliability
Cloud hosting spreads resources across multiple servers and data centers. It provides higher reliability and less downtime compared to traditional single-server architecture.
Even if one server fails, web requests are instantly routed to other servers to minimize any downtime.
4. Speed and Performance
By leveraging multiple servers and data centers, cloud hosting provides much faster performance compared to single-server hosting. Content is delivered from the server closest to the user’s location.
5. Security
Reputable cloud providers implement state-of-the-art security, including firewalls, intrusion detection, encryption, and regular software patches. This provides enterprise-grade protection of your data and applications.
6. Mobility and Flexibility
Cloud hosting allows seamless access to your website, content, and tools across both web and mobile apps.
Team members can collaborate from anywhere with just an internet connection.
The flexibility of on-demand provisioning and managed infrastructure also encourages innovation and agility.
Pros and Cons of Cloud Hosting
Of course, there are also some potential downsides and limitations to evaluate before adopting cloud hosting:
Pros
- Cost-effective pay-as-you-go model
- Nearly unlimited scalability for growth
- Maximum uptime and reliability
- Enterprise-level security protections
- Access applications from anywhere
- Get to market faster with rapid deployment
Cons
- Dependency on Internet connection
- Some loss of control over infrastructure
- Potential data protection and privacy concerns
- Multi-tenant architecture has vulnerabilities
- Hosting provider could have outage or go out of business
For most modern businesses though, the pros heavily outweigh the cons. Just be sure to partner with reputable and reliable cloud hosting providers.
Who Should Go for Cloud Hosting?

Here are some examples of websites and use cases that are perfect for cloud hosting:
- Startups – Scalable and cost-efficient for growing online business needs
- eCommerce sites – Handles seamless traffic surges during promotions or holiday sales
- Mobile apps – Access computing resources on-demand instead of managing own servers
- Data-driven sites – Leverage immense storage and databases available via cloud servers
- High-traffic sites – Scales seamlessly to accommodate growing visitor demands
- Software/SaaS companies – Quickly deliver applications to customers through cloud
- Media streaming services – Speeds up content delivery around the globe via CDNs
- Government agencies – Meet security and redundancy mandates more easily and cost-effectively
- SMBs and non-profits – Avoid large capital expenditures for physical infrastructure
Cloud hosting streamlines website management for organizations of almost any size.
It eliminates hefty upfront investments and allows convenient pay-as-you-go pricing aligned with your actual website usage.
With the ability to scale seamlessly and maximize uptime, cloud hosting is ideal for any website or web application.
It provides enterprise-level infrastructure and performance without the high costs of managing your own servers.
Advanced security, faster speed, high availability, and increased collaboration are some of the many benefits you can leverage by moving to the cloud.
Examples of Cloud Hosting
Many companies provide cloud hosting services.
Two major examples are Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
1. Amazon Web Services

AWS is one of the most popular public cloud hosting providers.
It offers services like data storage, computing power, databases, and AI/machine learning.
Companies use AWS in different ways – some to store files and data, some to run complex applications.
On Cloudways, AWS has pricing plans ranging from around $40 per month to over $3500 per month.
The more expensive plans provide faster speed or extra computing capability for companies with complex needs.
Even the cheaper plans still allow for storing huge amounts of data.
AWS Pricing Plans on Cloudways
- AWS Small – $38.56/mo
- AWS Medium – $91.84/mo
- AWS Large – $183.22/mo
- AWS XL – $285.21/mo
- and goes till AWS 24XL – $3569.98/mo
2. Google Cloud Platform

Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is Google’s cloud hosting solution. Like AWS, GCP offers computing power, databases, data analytics, and machine learning capabilities.
Many companies use GCP for advanced data analysis and AI projects.
On Cloudways, Google Cloud also has monthly pricing plans ranging from $40 to over $1500.
More expensive plans provide greater speed and more advanced analytics for companies working with huge datasets.
Google Cloud Pricing Plans on Cloudways
- GCE Small – $37.45/mo plan
- GCE Medium – $84.12/mo plan
- GCE Large – $152.14/mo plan
- GCE XL – $241.62/mo plan
- and goes till GCE HC 16XL – $1593.58/mo
Quick Note: we are also using Digital Ocean cloud hosting services from Cloudways. If you are going to make a purchase on Cloudways, make sure you use our Cloudways coupon code “BLOGGINGBEATS” that lets you save 25% on your first 3 invoices.
Overall, the key point is that major cloud providers like AWS and GCP allow organizations to conveniently perform computing and store data over the Internet.
And they offer varying price points based on factors like speed, storage space, analytics capabilities, and customer support.
Choosing the right cloud hosting provider depends on an organization’s specific business needs.
FAQs about Cloud Hosting
Here is a list of frequently asked questions about Cloud hosting that you may find useful.
Cloud-hosted software runs on servers owned by the cloud provider rather than on-premises servers, providing scalability, reliability, and reduced hardware costs.
Hosting runs on specific servers you own or rent, while cloud hosting uses a network of the provider’s servers, allowing flexible scaling and only paying for what you use.
Cloud can be cheaper than dedicated hosting because you only pay for the resources you use rather than needing to maintain physical servers that are underutilized.
Yes, Amazon Web Services (AWS) is the largest and one of the first cloud hosting platforms, providing infrastructure, storage, databases, and other services.
The best cloud hosting provider depends on your needs – AWS, Azure, and GCP are top options with global infrastructure, security, and scalability.
Also Read:
- Best Web Hosting Providers in 2024
- Best VPS Hosting Services To Grow Your Website in 2024
- Best Managed WordPress Hosting for Maximum Performance in 2024
- Top Reliable Web Hosts to Get Free .Com Domain for 1 Year in 2024
- Best Podcast Hosting 2024 to Create & Monetize Your Podcasts
- Managed Hosting vs Shared Hosting: Which Is The Best Fit For Your Website In 2024?
- Best Web Hosting Deals 2024: Save up to 90% on Reliable Services
- Top Sites To Buy Expired Domains in 2024
- Best Web Hosting Free Trials in 2024
Final Thoughts about Cloud Hosting in 2024
Cloud hosting has transformed web hosting with its flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency.
While factors like security and provider reliability must be evaluated, the pros seem to heavily outweigh the cons for most modern organizations.
As technology advances in 2024, cloud hosting will become even faster, more secure, and ubiquitous across nearly all industries.
Businesses that embrace the cloud stand to gain considerable competitive advantages.
With some careful planning, you can harness these benefits to successfully launch applications, store data, and power e-commerce sites directly in the cloud.